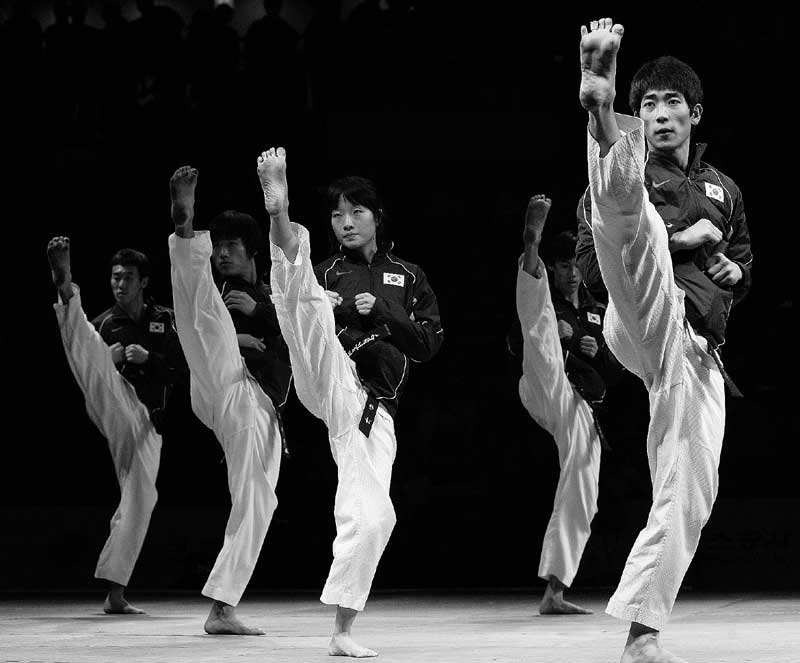
The forceful and finer techniques of attack and defence are largely denendent on a correct stance.Stability, agility, balance and flexibility are the controlling factors.
Basic principles for the proper stance are:
- Keep the back straight with few exceptions.
- Relax the shoulders.
- Tense the abdomen.
- Maintain a correct facing. The stance may be full facing, half facing or side facing the opponent.
- Maintain equilibrium.
- Make use of the knee spring properly.
Main stances
- Close stance (Moa sogi)
- Parallel stance (Narani sogi)
- Open stance(Palja sogi). Types: inner open stance (an palja sogi) and outer open stance (bakat palja sogi)
- Walking stance (Gunnun sogi)
- L-stance (Niunja sogi)
- Fixed stance (Gojung sogi)
- Sitting stance (Annun sogi)
- Diagonal stance (Sassun sogi)
- Crouched stance (Oguryo sogi)
- X-stance stance (Kyocha sogi)
- One-leg stance (Waebal sogi)
- Bending stance (Guburyo sogi)
- Vertical stance (Soojik sogi)
- Rear foot stance (Dwitbal sogi)
- Low stance (Nachuo sogi)
- Attention stance (Charyot sogi)
- Ready stance (Junbi sogi)
- Parallel ready stance (Narani junbi sogi)
- Open ready stance (Palja junbi sogi)
- Sitting ready stance (Annun junbi sogi)
- Close ready stance (Moa junbi sogi)
- Walking ready stance (Gunnun junbi sogi)
- Bending ready stance (Guburyo junbi sogi)
- L-ready stance (Nunja junbi sogi)
- X-ready stance (Kyocha junbi sogi)